Voëlvlei

Firstly, a few facts about this well-known birding spot near Mossel Bay – well-known if you are a birder that is, particularly one who has explored the birding delights of the southern Cape.
- ‘Voëlvlei’ can be directly translated from Afrikaans as “Bird wetland (or pan)”, although no one would ever call it that in South Africa. ‘Voël’ is of course the Afrikaans term for ‘Bird’ and ‘Vlei’ is a widely used term for any shallow body of water such as a seasonal wetland, shallow pan or marshy depression where water collects during the wet season.
- The pan at Voëlvlei only retains water during very wet years, which can be anything from 7 to 15 years apart, so when the vlei has water it very quickly becomes a magnet for waterbirds and waders, followed closely by many a keen birder out to find a variety of birds, with a strong possibility of a rare migrant wader or two during the summer months.
- Voëlvlei lies about 35km south-west of Mossel Bay and is on privately owned farming ground – the owners have generously allowed access to the vlei for birders as long as they behave in a respectful way.

- A track skirts the vlei on one side with entry possible from two farm gates at the northern and southern extremes (after entering or exiting it is good form to close the gate again).
My Atlasing Visits to Voëlvlei

The table above shows all my atlasing records since my first visit in December 2015 – green indicates that it was a “Full Protocol” card, which requires a minimum of two hours of intensive atlasing, the grey is for “Ad hoc” cards.
The good (or bad news depending on your inclination) is that I still have my journal records of all of the “green” cards, so join me as I return to those journals and select some of the highlights of the visits. You can, of course, skip the words and just look at the pictures, but I believe my readers are made of sterner stuff than that and are not afraid to plough through the verbiage.
14 and 18 December 2015
My first visit was 10 years ago, long before we moved permanently to Mossel Bay…
I had long read about the vlei as being a top birding spot when conditions were right. With reports trickling through of favourable water levels after good winter and early summer rains, I stopped at Voëlvlei on my way back from atlasing Gouritsmond, to find that it indeed had plenty of water and what appeared to be thousands of birds.
I did a quick list of some of the obvious birds, without going through the gate into the vlei area itself. A few days later Gerda joined me for a late afternoon visit to the vlei, when we entered Voëlvlei proper and followed the track around the east flank, then returned along the same route. The atlasing protocol allows a maximum of five days for one ‘card’ so I could add to the short list I had started on the 14th.
Birding was excellent and plentiful, the only downside being the sun in the west which created a sharp glare, making it difficult to see the birds clearly. We added 36 species to the initial 10 taking the total to 46, including ..
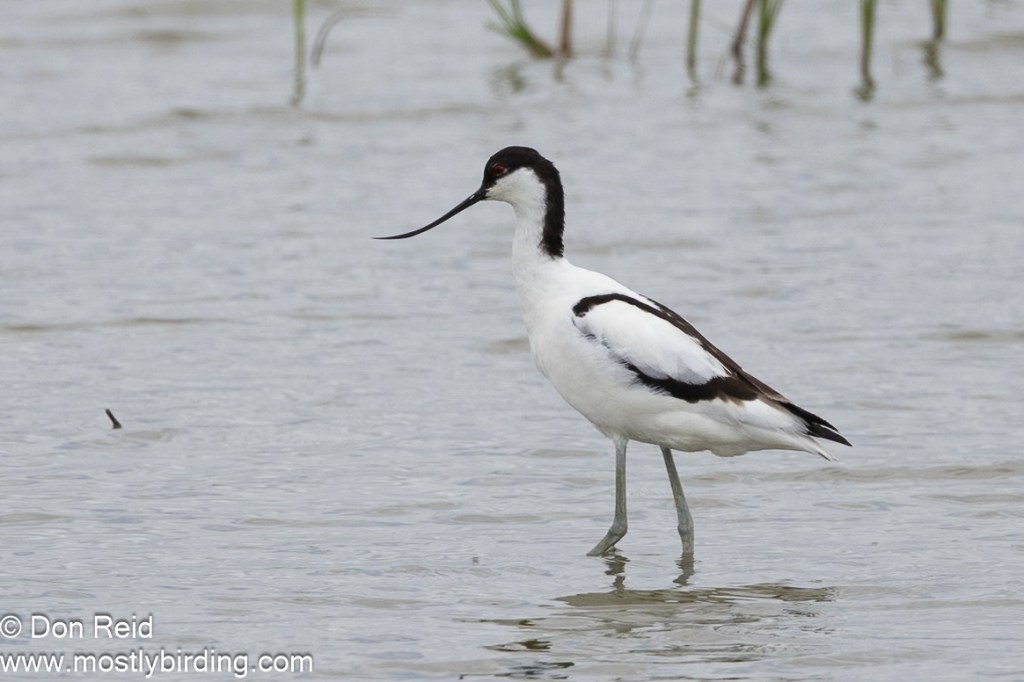
- Pied Avocet – notable for being a ‘Year bird’ for me (Birders are such nerds)

- Hundreds of Whiskered Terns

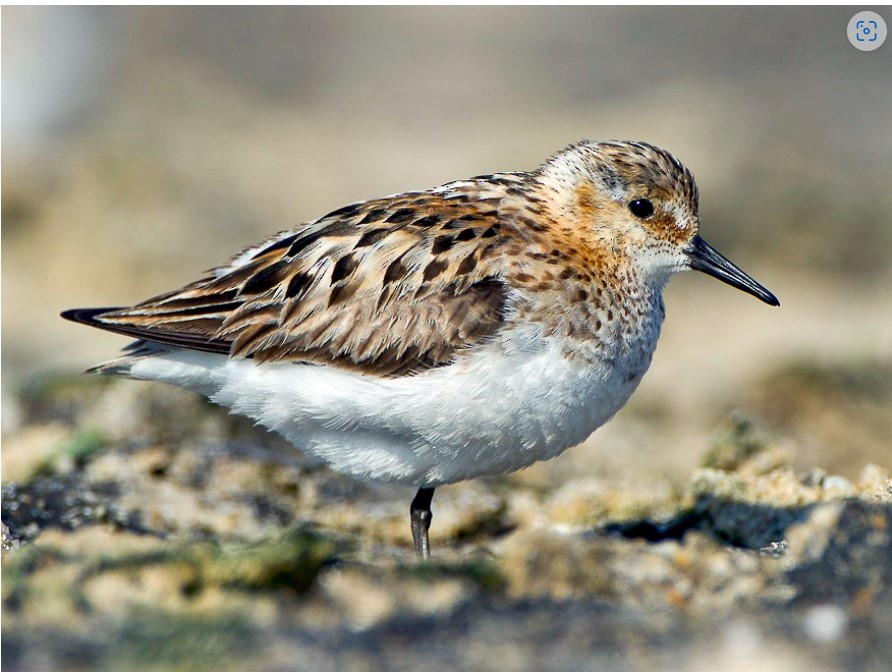
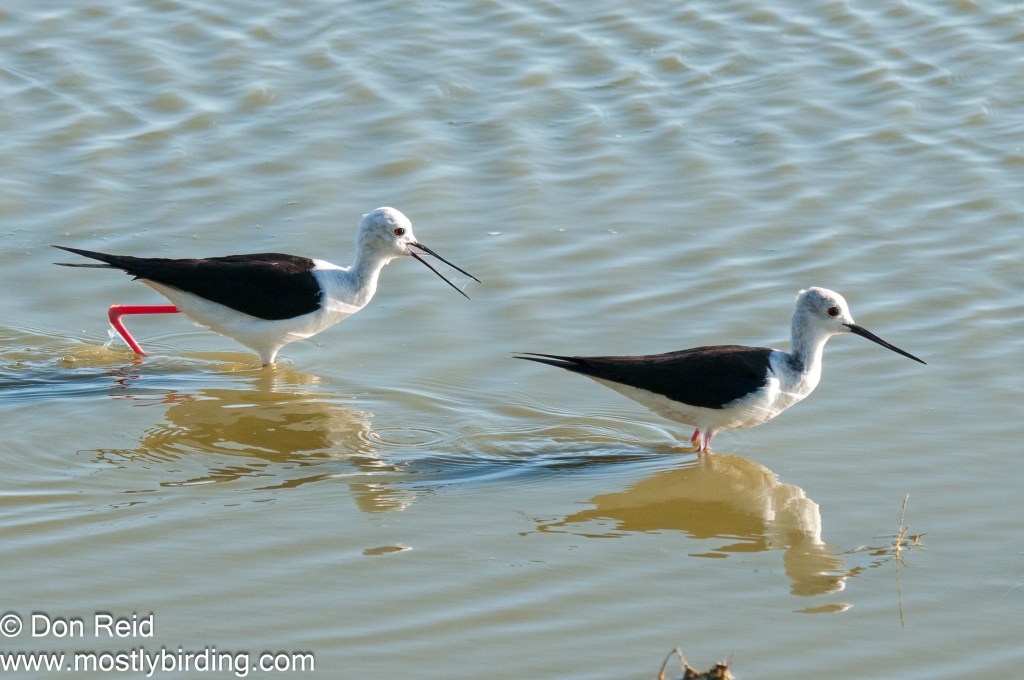
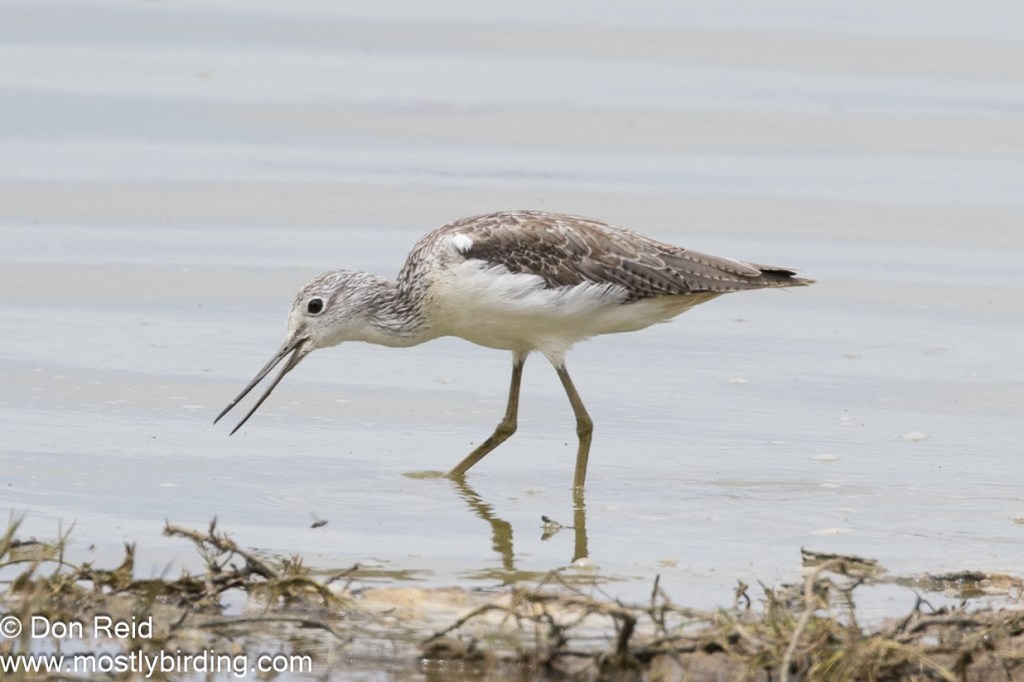
- Waders such as Little Stint, Black-winged Stilt, Wood Sandpiper, Three-banded Plover, African Spoonbill and Greenshank



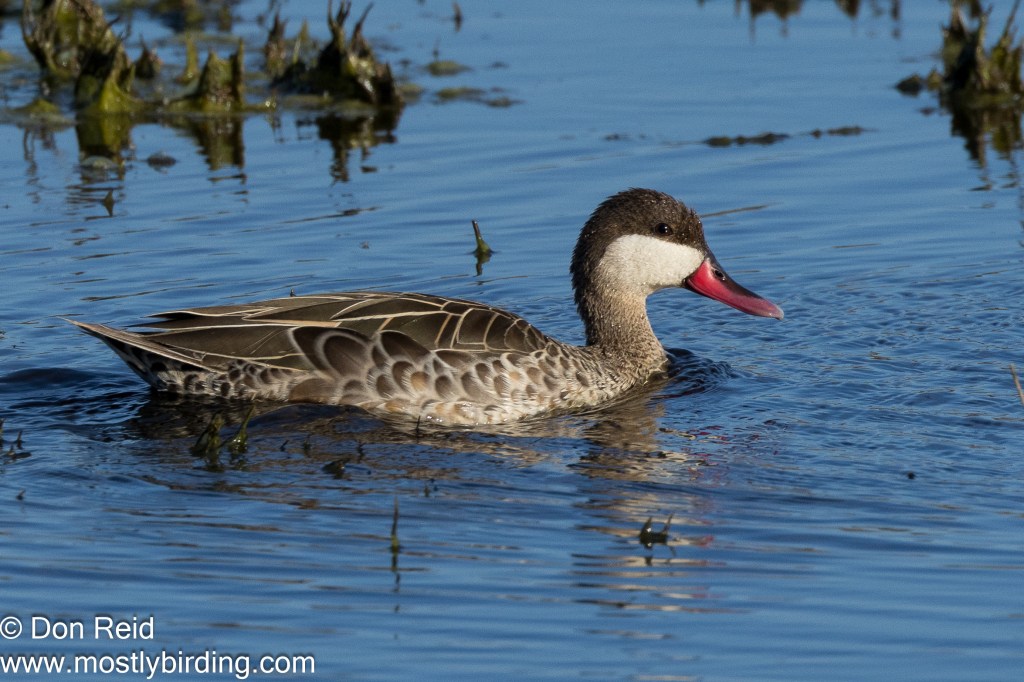
- Swimmers – Yellow-billed Duck, Red-billed Teal, Cape Teal, Southern Pochard, Cape Shoveler and Great Crested Grebe

- Booted Eagle soaring overhead
- White Stork
This first visit was particularly memorable – little did I know it would be eight years before I would experience something similar at Voëlvlei…
I did atlas the pentad in the intervening years but did not include Voëlvlei itself as it had dried up completely
30th November and 2nd December 2023
Having moved to Mossel Bay in October 2023 and seeing the reports of increasing water and bird presence at Voëlvlei, I was keen to visit the spot and see for myself. Reports of rarities made it even more imperative so I set off on the last Thursday of November, the day in the week that I have tried to keep open for atlasing.
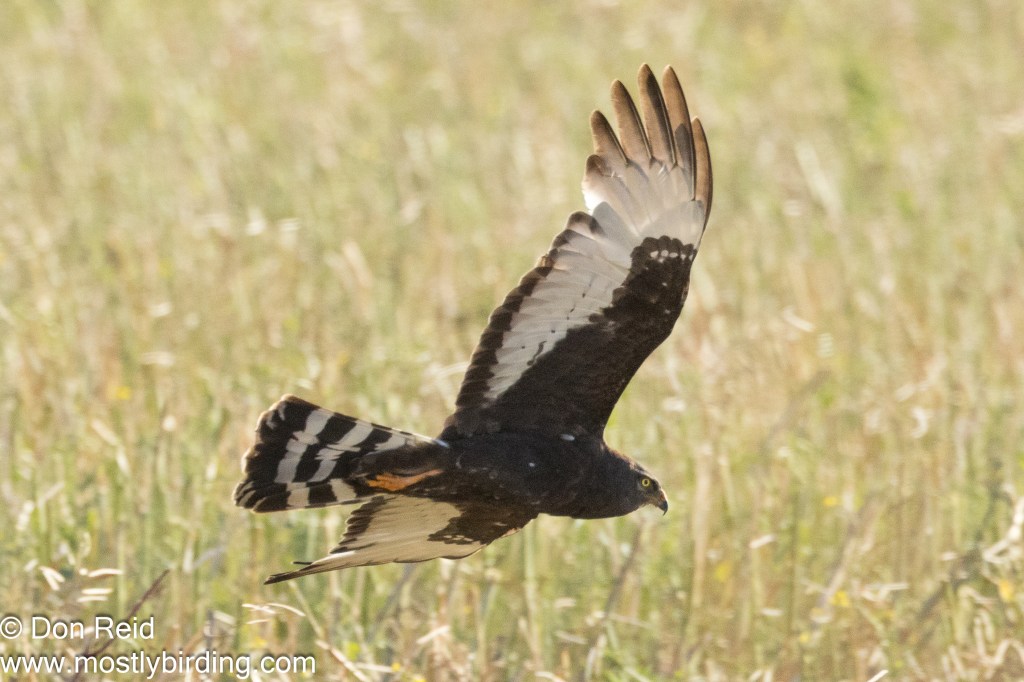
I started my pentad list along the road past Vleesbaai with a Black Harrier which I chased down the road to try and get level with it as it hunted low over the fields in true Harrier fashion, stopped quickly and rattled off a few shots – with limited success but lovely to see it in hunting mode.

Further on I took the turnoff to Voëlvlei and after passing through the gate I spent the next three hours carefully scanning the vlei from the track along the east flank, particularly the muddy margins which were teeming with birds.
The open waters towards the middle of the vlei as well as the surrounding dry land were equally busy with their particular species all enjoying a cornucopia of edible life.
Once again the waterbirds dominated my list …
- Waders – Black-winged Stilt, Three-banded, Kittlitz’s and Common Ringed Plovers, Little Stint (lots), Ruff, Wood Sandpiper, Grey Plover, Pied Avocet, Greenshank, Blacksmith Lapwing, Grey Heron, African Spoonbill and Little Egret
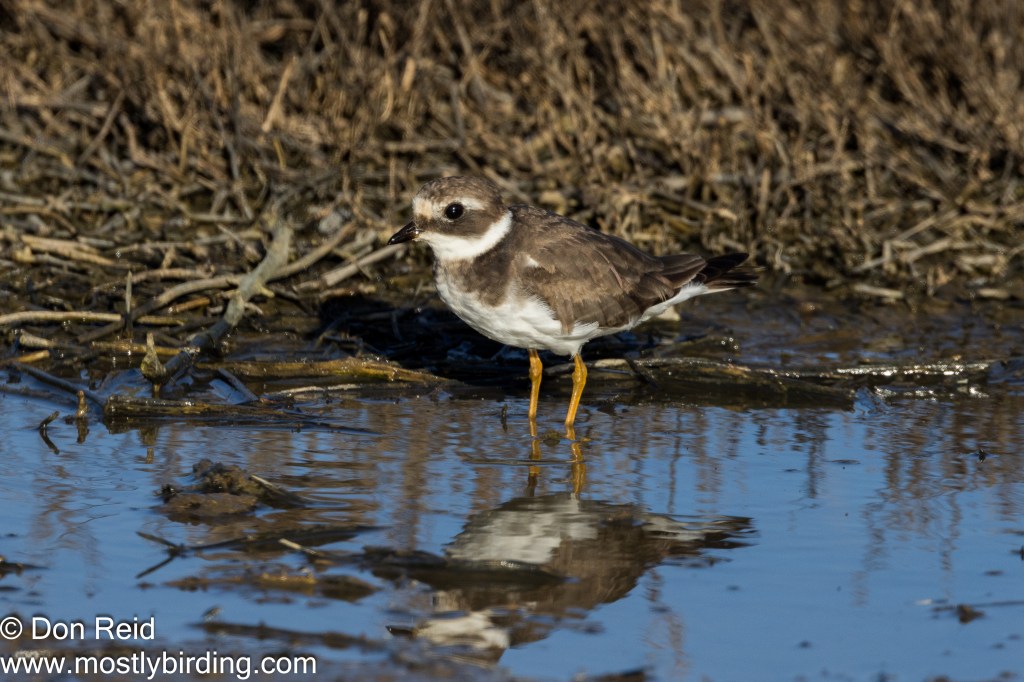
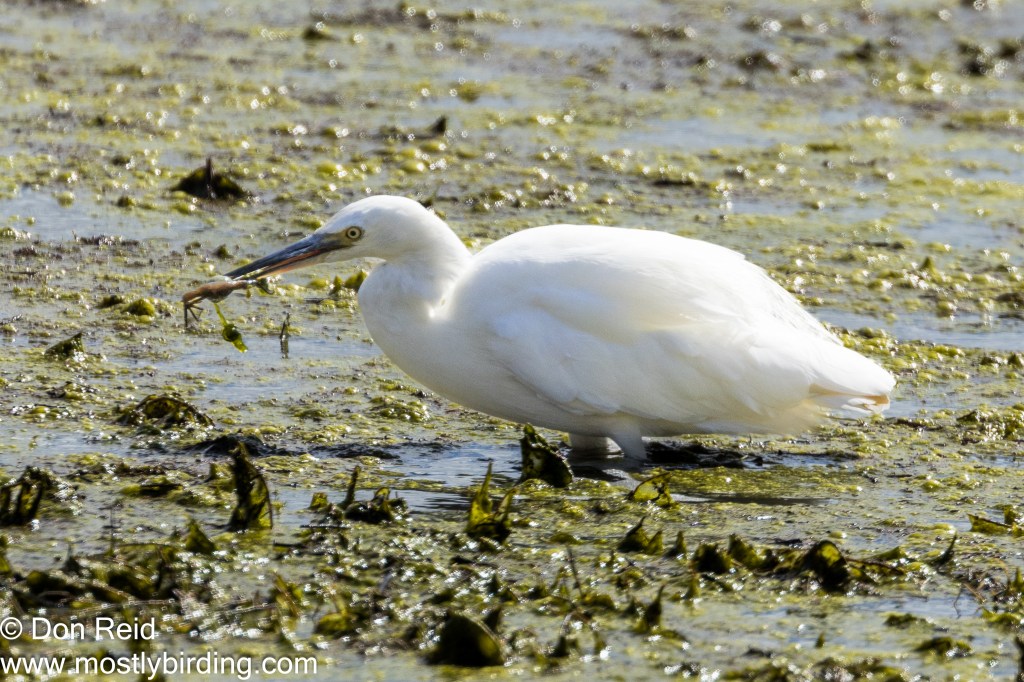









- Swimmers – Red- billed Teal, Red-knobbed Coot, Grey-headed and Hartlaub’s Gull, Cape Shoveler, Little Grebe and South African Shelduck.



- Rarities – This visit was excellent preparation for the annual Birding Big Day just two days later when many of the same birds were recorded by our team. An added thrill was seeing two rarities which had been spotted by some of the keen birders already present –
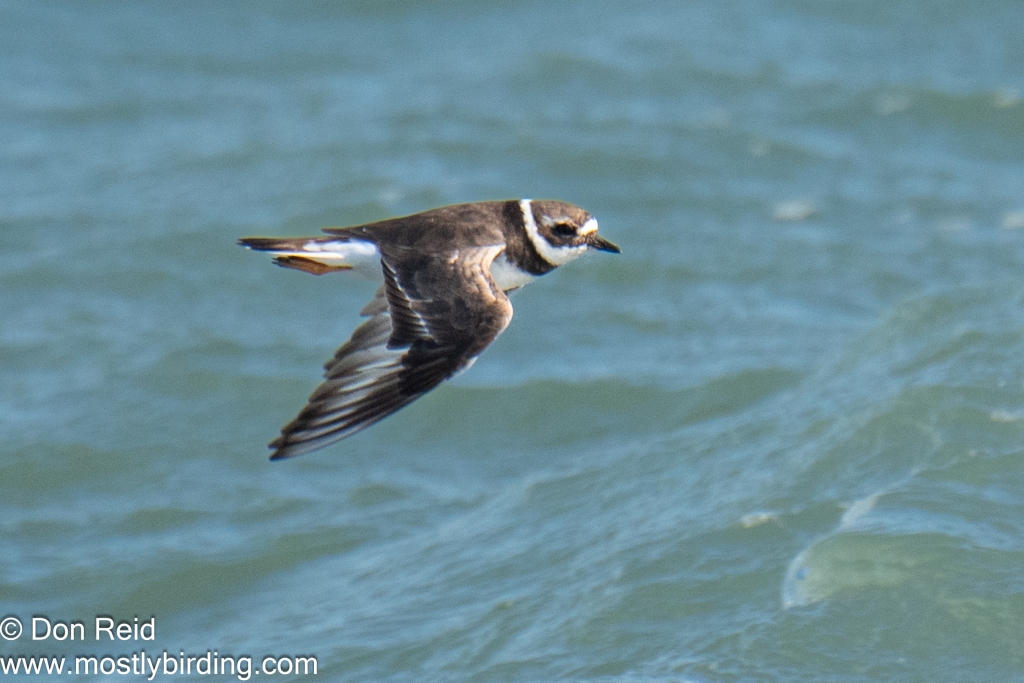
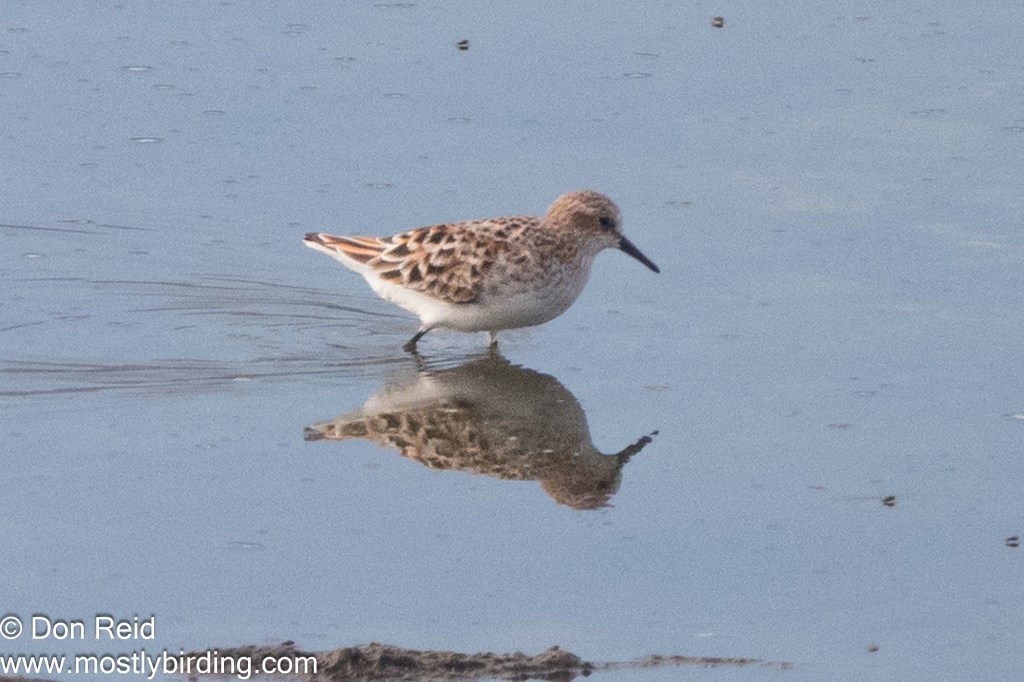
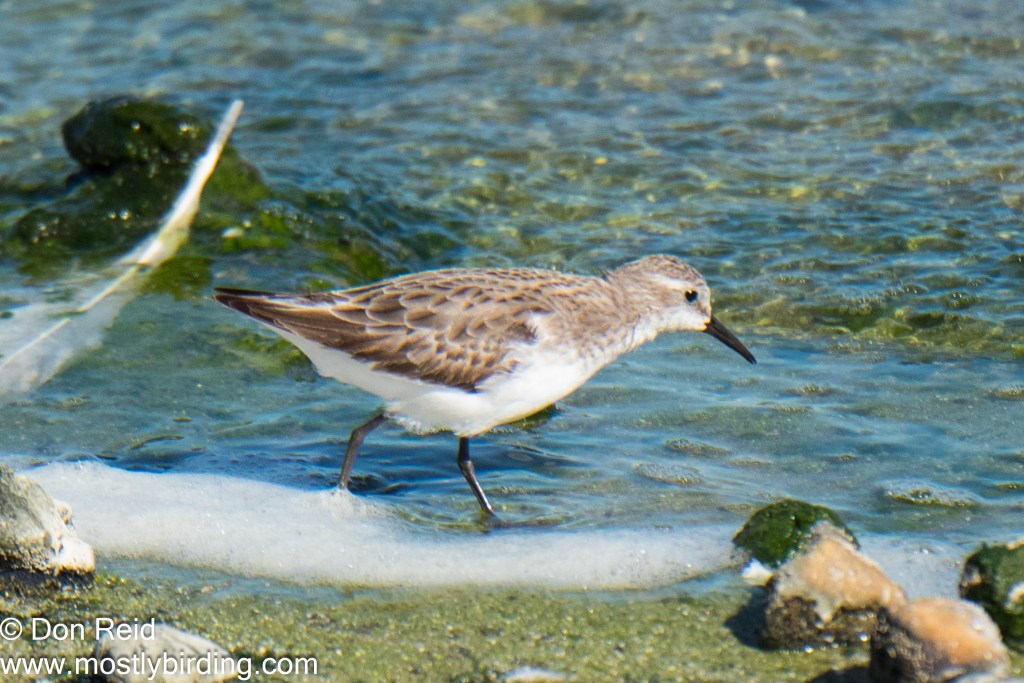
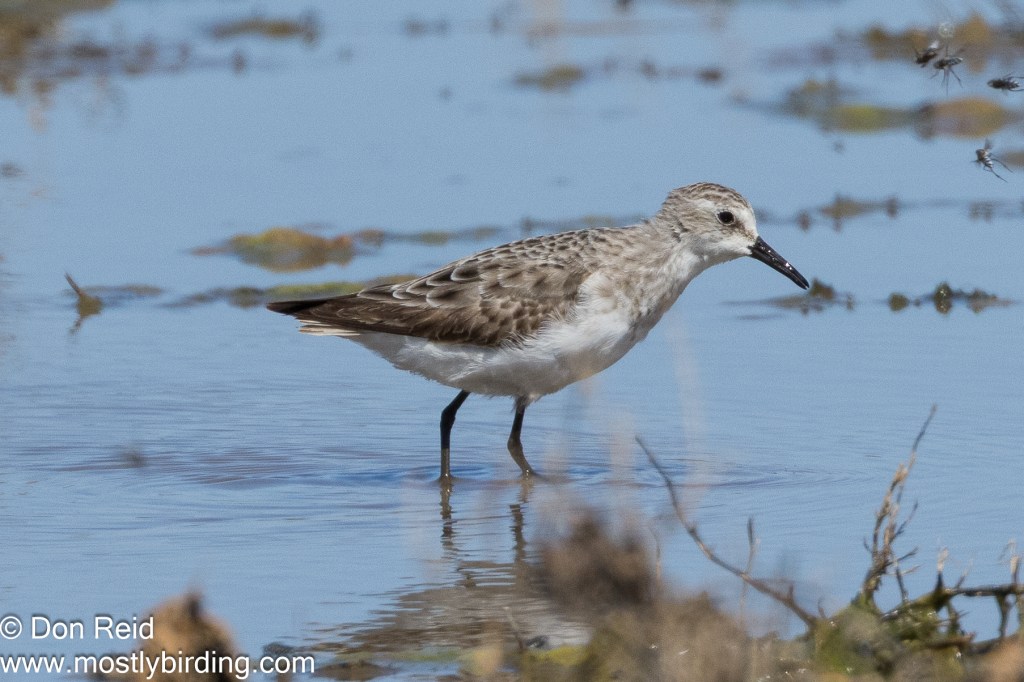
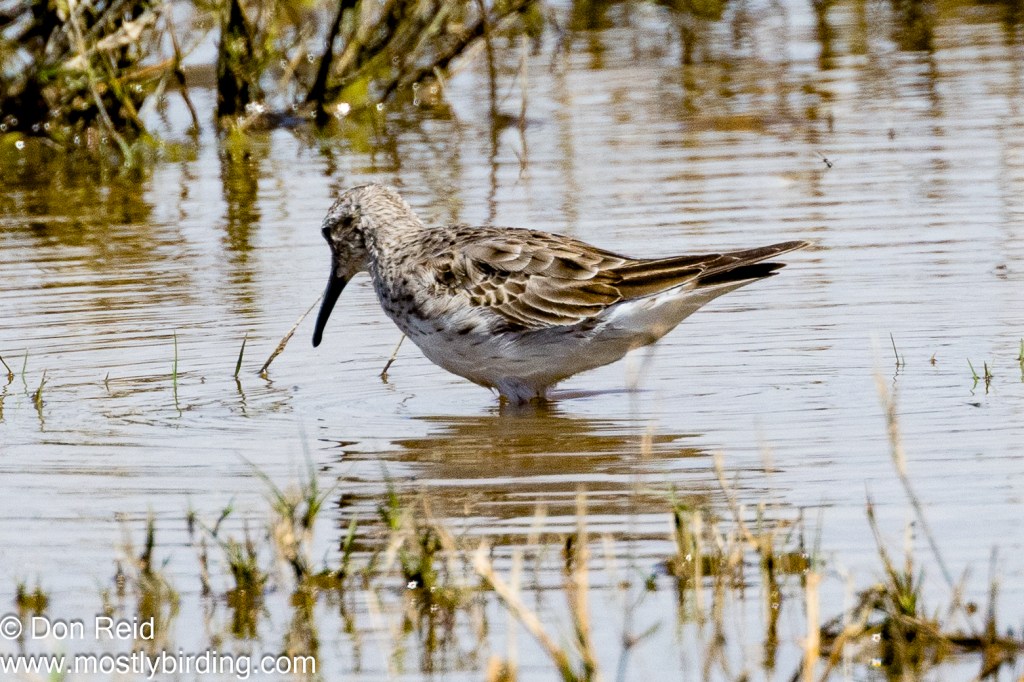
- White-rumped Sandpiper – a low-slung, longish-winged sandpiper, difficult to distinguish among the many small waders except when close to the many Little Stints present

- Western Yellow Wagtail – courtesy of one of the other teams who had it in their scope view and allowed us a quick look but it was too far for photos
An added pleasure was seeing a large flock of Greater Flamingos on the far side of the water –

10th to 13th December 2023
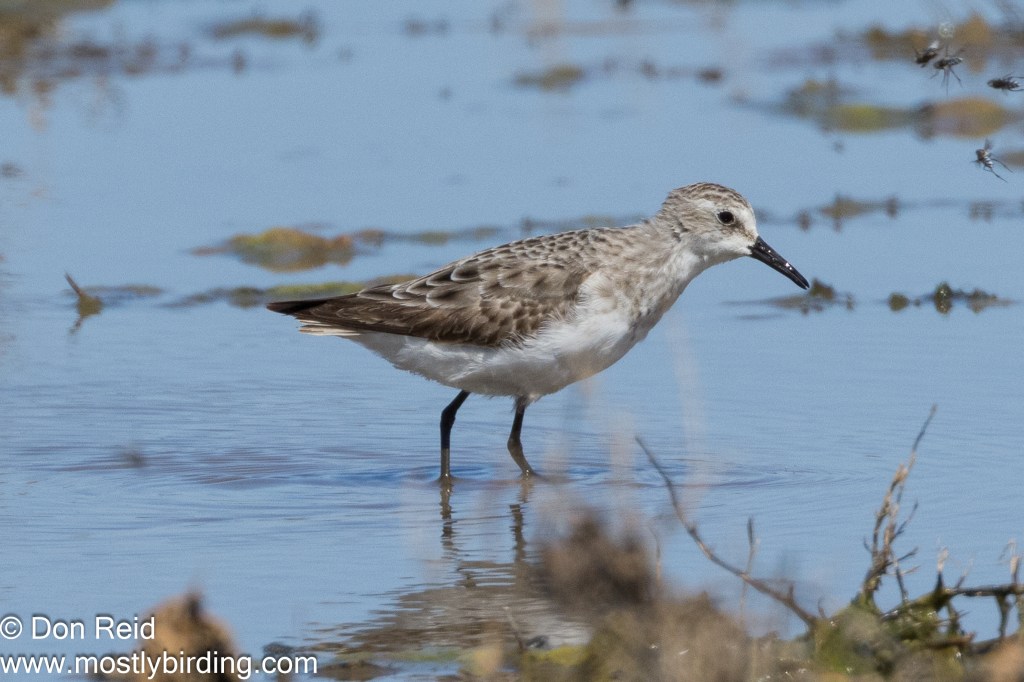
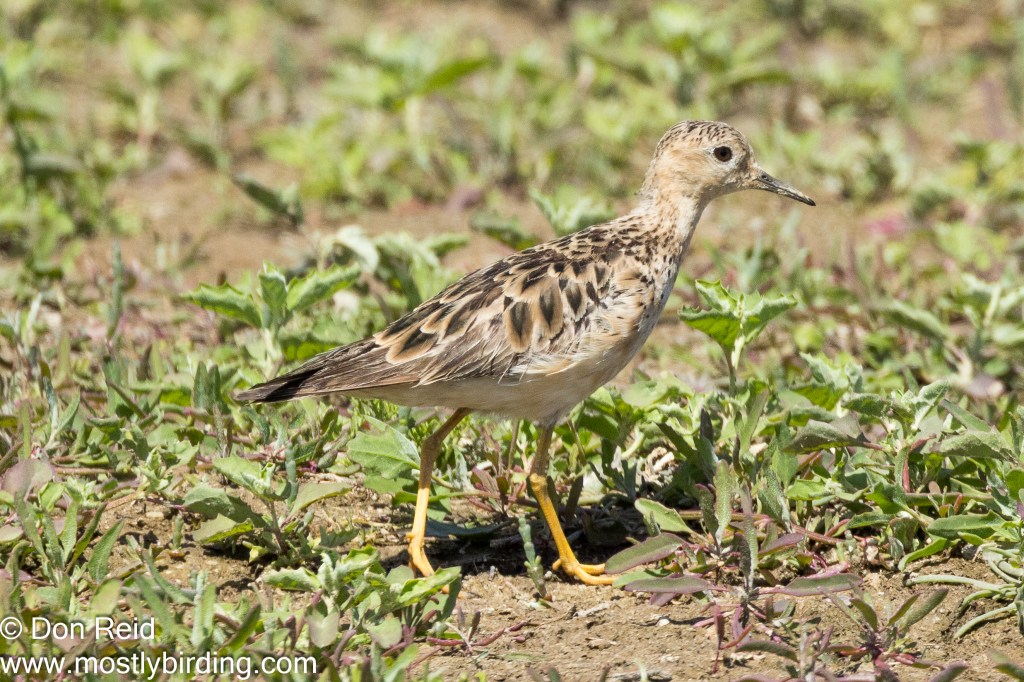
With Voëlvlei still attracting a lot of attention from birders and with reports of another rarity – Buff-breasted Sandpiper – being seen there, I couldn’t resist another visit just a week later.
It was a Sunday and Gerda agreed to join me, so after a traditional Sunday lunch at a country restaurant on the way (meat and three veg with rice plus a pudding) for not much money, we headed to Voëlvlei and joined several vehicles and birders with the same idea.
The Buff-breasted Sandpiper was quickly pointed out by those already present – on its own foraging in the dry, lightly grassed area away from the water – clearly a loner not interested in mingling with the many other waders in the vlei itself.
I spent a while scoping the sandpiper and taking photos of it from a distance, while recording all the other species present as they came into view.
We headed home with 34 species recorded. Feeling that the list needed boosting, I decided to include Voëlvlei in my next atlasing session on the following Wednesday, which would fall in the allowed 5 days for a “Full Protocol” card.
I arrived at the vlei mid-morning and spent three more enjoyable hours viewing the multitude of birds, adding a further 16 species to take my total to a nice round 50 for the pentad.
The White- rumped Sandpiper was still present and I spent some time trying to get better photos of this rarity – with limited success. It was difficult to get close enough to the bird, which remained among short grass tufts in the shallows of the vlei, intermingling with other waders and probing the mud constantly so that it was nigh on impossible to isolate it for a decent photo.
- Waders – Black-winged Stilt, Kittlitz’s and Common Ringed Plovers, Little Stint (lots), Ruff, Pied Avocet, Blacksmith Lapwing, Grey Heron, African Spoonbill, Little Egret, Cattle Egret, Glossy Ibis and Sacred Ibis

- Rarities – Buff-breasted Sandpiper, White-rumped Sandpiper

- Swimmers – Red-knobbed Coot, Red-billed Teal, Cape Teal, Cape Shoveler, South African Shelduck
- Others – Brown-throated Martin, Barn Swallow, Large-billed Lark, Red-capped Lark, Agulhas Long-billed Lark, Grey-backed Cisticola, Blue Crane, African Pipit, Capped Wheatear

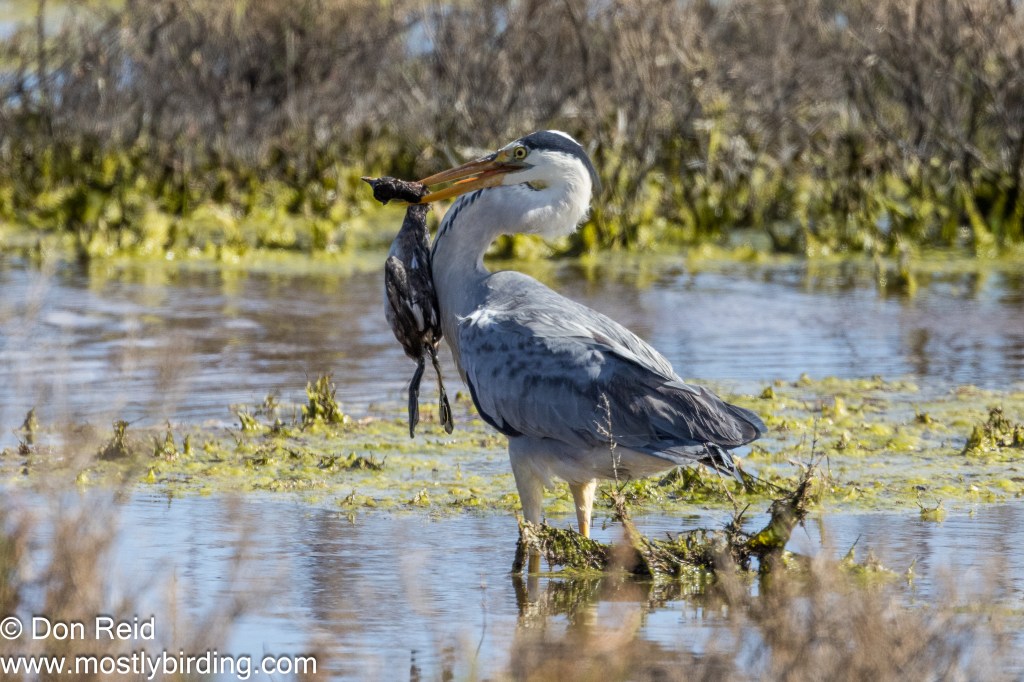
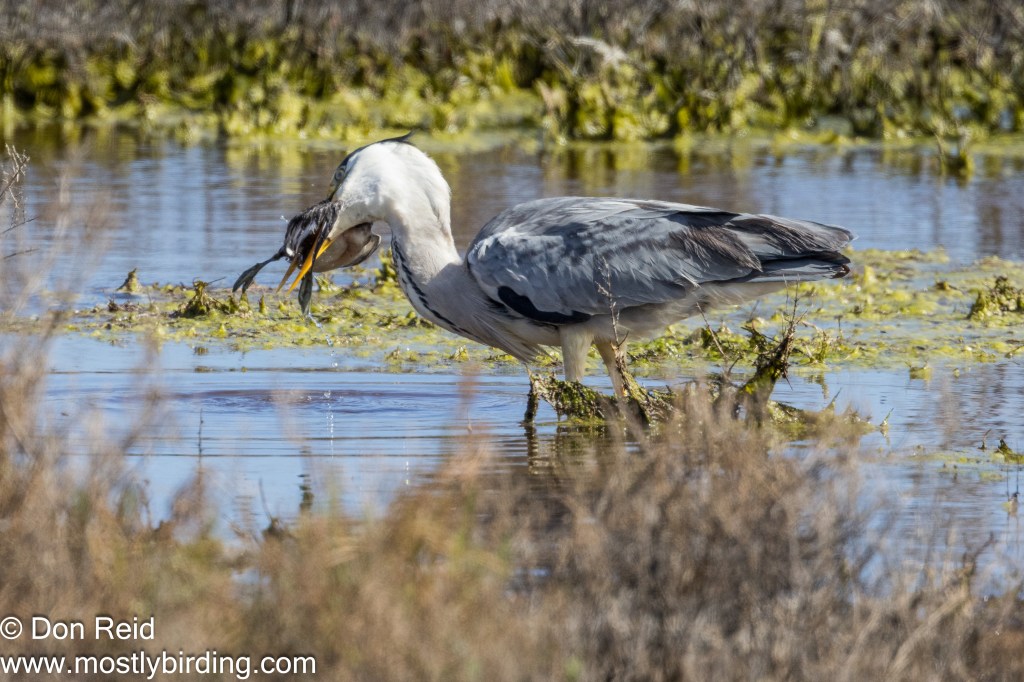
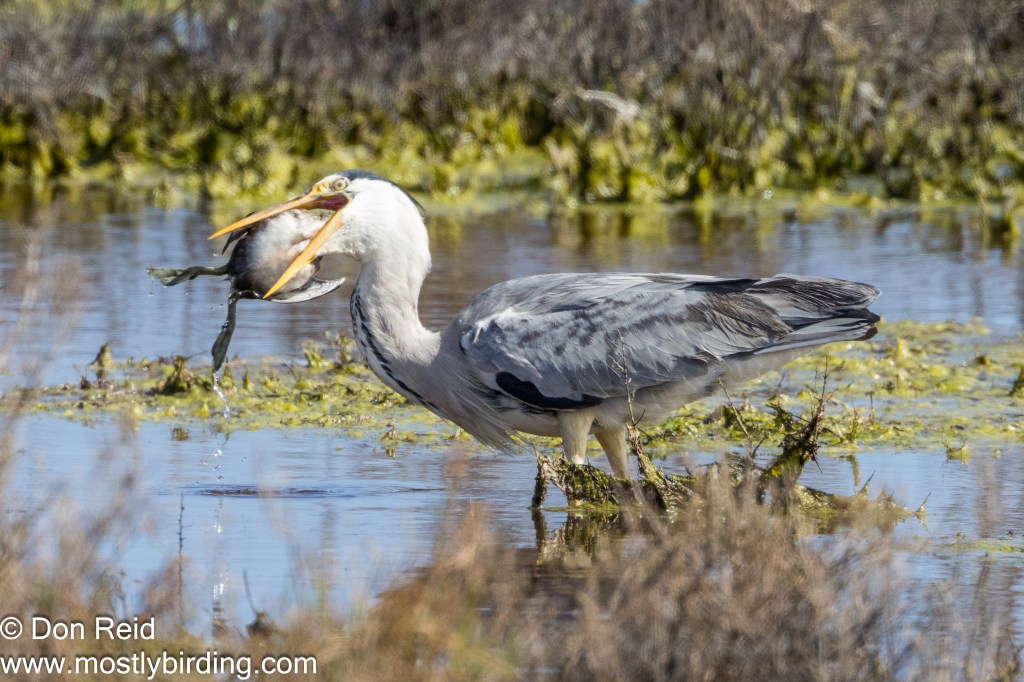
- Most Surprising Sighting? – most certainly seeing a Grey Heron with what looked like a Reed Cormorant (possibly a juvenile) in its bill, which it proceeded to manoeuvre into position and swallow whole! I wasn’t able to capture the final swallow as the Heron moved behind some reeds.



February 2024
The vlei remained partly inundated during the most of 2024, with water levels gradually decreasing as inflow dried up.
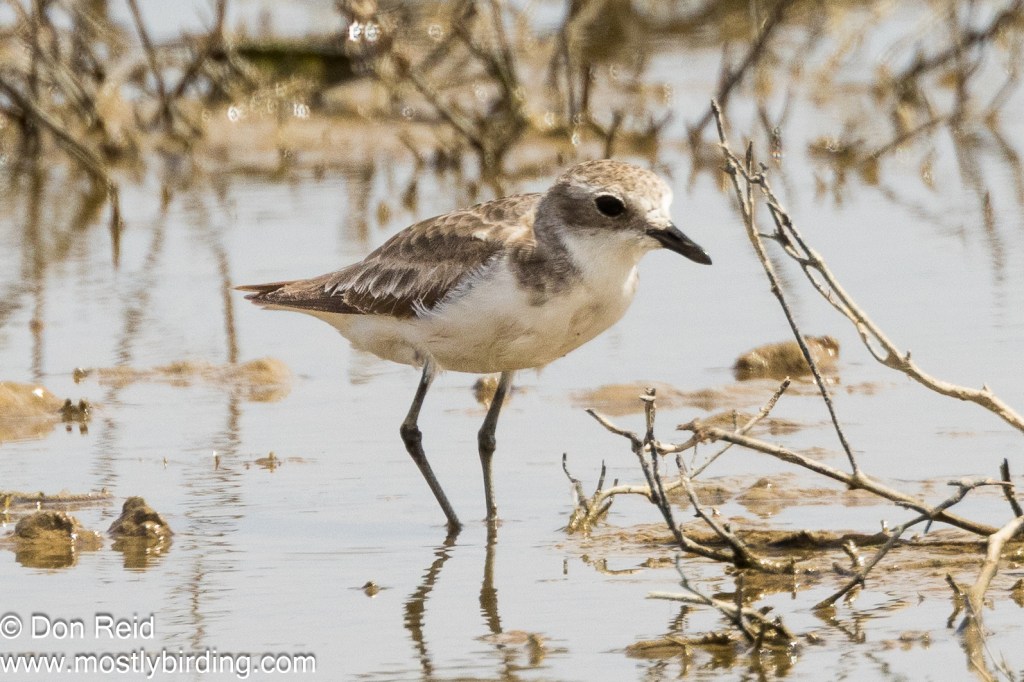
During February reports appeared on the local birding groups of a Greater Sand Plover at Voëlvlei – I had seen this species before but just once, so at the end of my next atlasing trip I took a detour to the vlei to see if I could find it.
At Voëlvlei I was able to find and photograph the Greater Sand Plover without too much effort and to record numbers of other waders which were still plentiful.

Thereafter the vlei gradually dried up, leaving ever wider margins. This did not come as a surprise for those living in the Southern Cape as it has been a particularly dry year for the area.
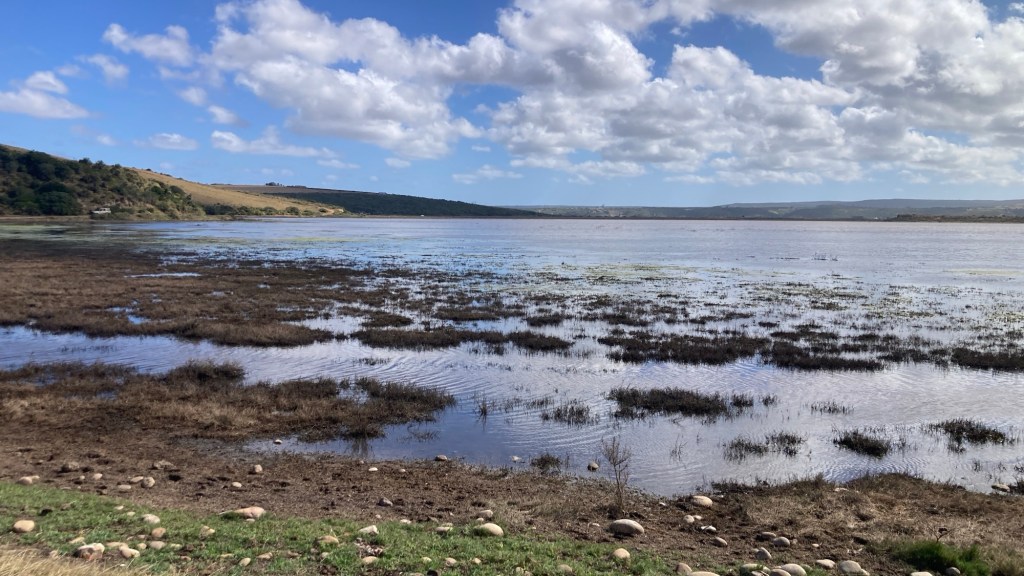
The photo below was taken in July this year, with just the northern section having any water – a couple of weeks after this photo the vlei was bone dry.

That just raises the question that is impossible to answer – when will Voëlvlei have water again? If average statistics are anything to go by it may be 7 or more years before that happens, a sobering thought at my age, I have to say, but I am thankful to have enjoyed two bountiful birding seasons during the last 10 years.